We have created all the conditions for the most modern and accurate diagnosis to be comfortable and accessible for you
Qualitative diagnosis allows detecting the disease in the early stages of its development, which allows for more gentle, painless, and high-quality treatment and eliminates errors in diagnosis.
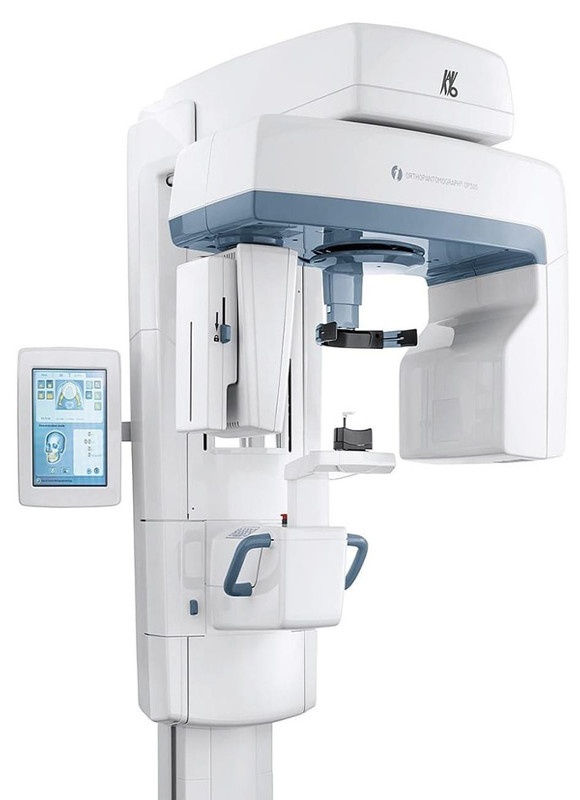
- Careful data collection.
- Periodontogram - a table that includes data on the condition of each tooth (the degree of mobility of the tooth, the attachment of the gums, the depth of the tooth pocket, the presence of dental plaque). Collecting such data 1-2 times a year makes it possible to objectively assess the condition of the teeth, and in the future - the effectiveness of treatment.
- X-ray diagnosis (sighting image) makes it possible to assess the structure and number of bones of one tooth, to control the quality of endodontic treatment.
- The panoramic image allows you to visually and simultaneously see the condition of all teeth, assess the structure and number of bones, anomalies of the dentition, the presence of hidden carious cavities, the condition of periodontal tissues, bone structure, and its number in place of previously removed teeth and more.
- Teleradiography - panoramic radiography of the skull in lateral and frontal projections. It is used to plan orthodontic treatment for various occlusion anomalies, prosthetics, and maxillofacial operations. Gives the chance of the exact diagnosis, drawing up of the plan of treatment with the subsequent estimation of results and terms of treatment.
- Computed tomography is a layered X-ray evaluation of the patient's dental and maxillofacial system. Thanks to it, you can get accurate data on the condition of bone tissue and its density. Without this study, dental implantation cannot be planned. It is also used to plan and diagnose developmental abnormalities, injuries, fistulas, tumors, various inflammatory diseases.
- Professional photo session before and after treatment allows for quality diagnosis, control, and quality of treatment at all stages with a clear demonstration of the result.
- Laboratory diagnosis provides data on the general condition of the body and other related factors that may affect the condition of oral tissues.
- Comprehensive orthodontic diagnostics using special computer programs.
Equipment
- SURGIC PRO OPT physiodispenser with 20: 1 titanium tip and LED backlight (NSK, Japan) for surgical dentistry and implantology procedures.
- E&Q Master system for three-dimensional root canal obturation.
- The quality of preparation of the tool before sterilization largely depends on the qualifications of the worker. We have eliminated the risk of manual cleaning: the MELAtherm heat-disinfecting washing machine completely automates the process of disinfection and cleaning of the tool.
- Digital compact tomograph HYPERION X9 3D (MyRay, Cefla) KPKT (cone-beam computer 3D tomography). With this device, one scanner reproduces a lot of data (75 microns) in high resolution. We are expanding the boundaries of our practice thanks to a new generation of diagnostic images. We use the high-frequency 3D-panoramic image, which allows you to get a full range of high-quality images of high resolution: orthogonal projections of teeth, biting X-rays, 3D images with the ability to view the mandibular joints, and maxillary sinuses.
- Centrifuge EBA 200 desktop - allows you to perform the procedure of plasma lifting.
- Ultrasonic surgical system (piezo) NSK VarioSurg LED.
Areas of application:
- a. bone surgery;
- b. sinus lifting;
- c. periodontology.
What gives this system:
- a. Lack of discomfort for the patient due to safe and gentle cutting of bone tissue;
- b. Easier recovery process after surgery due to the absence of soft tissue damage;
- c. Safety, because the operation of the device is based on the principle of "selectivity". Only skeletal tissue is cut, and soft tissues, including nerves, sinus membranes, and blood vessels, are not affected and therefore not damaged;
- d. Ability to perform operations in hard-to-reach places of the oral cavity;
- e. Additional antiseptic treatment of the wound due to the antibacterial effect of ultrasound;
- f. High accuracy of manipulations and the expected result;
- g. Low incidence of complications;
- h. Reducing the duration of the operation.
Our department deals with a wide range of diseases: Teeth:
- Caries - is characterized by the appearance on the enamel of pigment spots from white to yellow-brown, bad breath, tooth reaction to sour, sweet, cold, hot food, aching pain that quickly disappears after the removal of the irritant.
- Treatment: professional oral hygiene if necessary and restoration of the tooth surface by filling due to a defect. Dentist.
- Pulpitis - characterized by paroxysmal pain that spreads to the entire jaw, worsens mainly at night, as well as from temperature stimuli (cold, hot); does not disappear after their removal.
- Treatment: diagnosis and elimination of the inflammatory focus by antiseptic treatment and filling of the root canal system. Dentist-endodontist.
- Periodontitis - bleeding and inflammation of the gums, pain when pressed, bad breath, mobility of teeth of varying degrees, which eventually leads to complete loss of the tooth.
- Treatment: often complex. Dentist-periodontist: thorough professional oral hygiene, instrumental curettage with the appointment of local antibacterial drugs, and general medical treatment. In cases of more severe periodontitis, the dentist performs the following surgical manipulations: open curettage, patchwork, and if it is impossible to save the tooth - its removal. In the future, the missing tooth should be restored with an artificial orthopedic structure. This may be an implant (performed by a surgeon) followed by prosthetics on the implant. Orthopedic doctor.
- Enamel hypoplasia - a change in aesthetic appearance due to changes in the shape and appearance of the tooth, the presence of whitish or depigmented areas, grooves, depressions.
- Treatment. Depending on the extent of the lesion, treatment is carried out by · dentist-therapist - by filling the defects, if they are small; · Dentist-orthopedist - if the defects are large, then orthopedic treatment is performed with the installation of ceramic crowns.
- Dental plaque - a dense plaque of yellow-brown color on the neck of the tooth and root. Bad breath and bleeding gums are common causes of caries, gingivitis, periodontitis with subsequent tooth loss.
- Treatment: professional oral hygiene. Dentist
- Pericoronaritis (wisdom tooth) - severe pain in the area of the erupting tooth, the limited and painful opening of the mouth, pain when swallowing, swollen gums, bad breath, malaise.
- Treatment: wisdom tooth removal, the appointment of general drug therapy. Dentist-surgeon
Pathological processes of the maxillofacial area:
- Cysts - often do not cause any symptoms and are detected in diagnostic tests.
- Treatment: · conservative (without surgery) - by medical rehabilitation of the root canal system and their filling. Dentist; · Surgical - cystectomy, and resection of the root apex. Dentist-surgeon.
- Defects of the dentition - masticatory disorders, displacement of teeth, gradual atrophy or deformation of the jawbones, a noticeable cosmetic defect. Defects contribute to impaired speech and loss of healthy teeth.
- Open bite - characterized by the absence of vertical overlap and closure of the upper and lower teeth. This is one of the most complex anomalies that is difficult to treat. Therefore, it is especially important to prevent the formation of open bites, which include: · elimination of bad habits - sucking a finger, nipple; · Timely diagnosis and correction of the size and position of the tongue. Another important factor influencing the development of open occlusion is oral respiration, which occurs due to impaired patency of the upper respiratory tract. At the same time, there is a low position of the tongue, insufficient development of the upper jaw.
- Treatment of open bite depends on the age of the patient and the causes of the pathology. In cases involving trauma that affects the articular processes, do not do without surgical care. Treatment of open occlusion may include tooth extraction, the use of multi-loop arches, orthognathic surgery.
- Medial occlusion is a facial deformity characterized by the anterior position of the lower jaw relative to the upper. Depending on the type of growth and the period of occlusion, a treatment plan is developed, which may include different stages: from observation to orthognathic surgery.
- A deep occlusion is a bite option where the upper incisors overlap the lower incisors by more than half the height of the crown. This situation can lead to abrasion of the incisors, injury to the mucous membrane of the palate, and aesthetic problems. Today there are various methods of correction of deep bite. The choice of strategy is based on the analysis of facial aesthetics, the length of the upper lip, and the height of the crowns of the incisors.
- Cross-bite - pathology of the bite with a mismatch in the size, shape of the dentition of the upper and lower jaws and their ratio. It is often accompanied by facial asymmetry and changes in the TMJ. Requires early correction to remove the blockage of growth and development of the dental apparatus.
- Distal occlusion is the most common of the European race. It is often formed as a result of prolonged mouth breathing and narrowing of the upper jaw. A distinctive feature is the posterior position of the lower jaw or the anterior position of the upper, or a combination of both. Patients with distal occlusion often complain of crowding of teeth, unsatisfactory facial aesthetics. Orthodontist.
Inflammatory processes of the oral mucosa:
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums that is characterized by bleeding and pain during home hygiene and eating solid foods. Occasionally there is a bad breath. This is a reversible condition that can be corrected by timely treatment at a dental clinic to obtain quality care and mandatory correction of individual oral hygiene. The stage of manipulation and the necessary methods of treatment are determined by the dentist by the clinical situation. The main method of eliminating this disease is professional oral hygiene. Occupational hygiene begins with a screening test to assess the extent of the disease. Additionally, information is collected on the presence of local and systemic factors that affect the course of the disease. Based on the data obtained, treatment tactics aimed at eliminating or minimizing the causes of gingivitis are determined. The purpose of this manipulation is to remove dental plaque from the surface of the teeth, which cannot be removed at home. To remove tartar and biofilm, we use ultrasonic and manual scaling, air-powder treatment of the tooth surface, and polishing the surface-pastes of different abrasiveness in combination with disposable polishing nozzles. The dentist also adjusts home oral hygiene by selecting cleaning products and methods that will help the patient take the best care of their teeth. Treatment: diagnosis, professional oral hygiene, plasma lifting, training in proper hygiene. Dentist-periodontist.
Periodontitis is the next stage of gingivitis. The reasons for its occurrence are a set of local factors (the presence of dental plaque) and the general condition of the body, which indicates the need for a comprehensive approach to treatment. The clinical manifestation includes all the same symptoms as in gingivitis, with the addition of tooth mobility, pain when biting food, as well as exposure to the root surface. The absence of timeliness or lack of proper treatment of periodontitis leads to tooth loss, so careful diagnosis and early detection of the disease increase the chances of a successful prognosis in the rehabilitation of the patient. To qualitatively approach the treatment of periodontitis, it should be remembered that this disease occurs due to the interaction of pathogens in the oral cavity and disorders of the general condition of the body. Therefore, various diagnostic methods are used to determine the cause, as well as the degree and stage of development of the disease. Comprehensive treatment of the disease is carried out with the involvement of related physicians and specialists. The patient's data on the development of the disease and possible heredity are carefully collected. X-ray diagnosis makes it possible to assess the structure and quantity of bone and tooth. The periodontal chart shows the presence and amount of dental plaque, bleeding gums, tooth mobility, and the degree of loss of fixation in the bone. Laboratory diagnosis provides data on the general condition of the body and other related factors that may affect the condition of the tissues of the oral cavity. Tactics of treatment are always determined individually, based on the results of research. The main manipulations are aimed at cleaning and polishing the tooth surfaces from dental plaque, as well as correcting common factors that may affect the progression of this disease. It should be remembered that the treatment of periodontitis is always a complex work of the doctor and the patient, which is aimed at eliminating the main causative factors of the disease, as well as maintaining the result with good personal hygiene.
- Stomatitis. Its signs: the mucous membrane of the mouth is swollen, hyperemic and painful, pain when eating, bleeding, bad breath. Treatment: accurate diagnosis, conservative methods of treatment - elimination of causative factors, local treatment in the form of rinses and irrigations, teaching the patient proper hygiene. Dentist-periodontist.
- Periimplant mucositis - inflammation of the gums around the implant.
- Periimplantitis is the next stage of periimplant mucositis. Includes inflammation of the gums, implant mobility, and reduction of bone tissue around the implant. Given modern technologies and methods of implantation, the percentage of such diseases is quite small. The main cause of such diseases is the deterioration of oral hygiene and general health. The clinical manifestations of these diseases are very similar. There is bleeding and soreness of the gums near the implant during home hygiene, the mobility of the implant when biting food. The main methods of diagnosis are X-ray examination of the bone with dental implants, as well as the collection of data on bleeding, the presence of dental plaque, the shape of the crown on the implant. Treatment of these diseases consists of eliminating the cause of inflammation and subsequent polishing of the implant surface. It is worth remembering that the care of implants requires careful compliance with individual oral hygiene, as well as regular visits to the dentist.
Methods of treatment
Parodontology
- Functional diagnosis of occlusion.
- Conservative: removal of dental plaque, scaling, plasma therapy, medical treatment.
- Surgical: open curettage, closed curettage, patchwork.
- Comprehensive treatment of periodontitis.
Anesthesia
- Application anesthesia.
- Injection anesthesia.
- Treatment under general anesthesia of children and adults.
- Medicated sleep.
Surgical operations
- Tooth-preserving: cytotomy, cystectomy, resection of the root apex.
- Elongation of the crown of the tooth.
- Plastic bridle of the tongue.
- Plastic bridle of the upper lip.
- Tooth extraction of any degree of complexity.
Osteoplastic surgery:
-
Closed sinus lifting;
- Open sinus lifting;
- Osteoplasty of the tooth cavity;
- Plasticity of the alveolar ridge.
- Tooth implantation.
Therapeutic treatment
- Sealing of carious cavities of any localization.
- Treatment of caries in the stage of stains without drilling cavities system Icon.
- Comprehensive treatment of pulpitis.
- Comprehensive treatment of periodontitis.
- Treatment under a microscope.
Aesthetic dentistry
- Professional hygiene.
- Teeth whitening.
- Tooth restoration.
- Veneers (ceramic restorations).
Dental prosthetics
Crowns:
-
a. Temporary;
- b. Metal-free ceramic crown;
- c. Metal-ceramic;
- d. Solid cast;
- e. Crown on the implant.
- Bridge prostheses.
- Removable dentures.
- Removable dentures on implants.
- Fixed prostheses on implants.
Treatment of children
- Hygiene lesson.
- Sealing of fissures.
- Treatment of caries of deciduous teeth.
- Dental treatment system without drilling cavities system Icon.
- Removal of deciduous teeth.
- Trimming the bridle of the tongue.
Orthodontics
- Bracket systems treatment:
a. Classic metal bracket system;
b. Lingual brace system;
c. Self-ligating;
d. Sapphire.
- Treatment with transparent caps (liners).
- The course of orthodontic treatment - management of the patient from the moment of installation of bracket system:
a. monitoring the dynamics of change;
b. customer service in the process of wearing the system;
c. teaching the patient to care for braces;
d. replacement and correction of orthodontic arches;
e. professional hygiene;
f. execution of dynamic OPTG;
g. bite correction;
h. system removal;
i. installation of retention apparatus.
- The course lasts an average of 1.5 to 2.5 years.
- Bracket activation and correction is a condition in which the system acts on the teeth, aligning them. It is performed by an orthodontist monthly or once every 10 days.
 Diagnostic and treatment planning
Diagnostic and treatment planning Aesthetic dentistry
Aesthetic dentistry Teeth whitening
Teeth whitening Therapeutic dentistry
Therapeutic dentistry Surgical dentistry
Surgical dentistry Orthodontics
Orthodontics Periodontology
Periodontology Pediatric dentistry
Pediatric dentistry Own anesthesia department
Own anesthesia department